

There are also good reasons why we could implemant AB Testing with Power BI: So through this post, I want to share the hidden or little known great capabilities of the Power BI statistical functions. Obviously, Power Bi is not R, Python or SPSS but I file like the builtin DAX Statistical Functions are just amazing and often under looked.
#Hypothesis test calculator to find z score how to
The main reason I decided to write this post is that I couldn’t find any post on how to implement AB testing with Power Bi with DAX so I thought it would be interesting to try out the advanced statistical functions of DAX. AB Testing with Power BI Why using Power Bi instead of R/Python? The metrics for conversion are unique to each website.įor eCommerce, it may be the sale of the products, while for B2B, it may be the generation of qualified leads.įor example, an online retail company wants to test the “ Hypothesis” that if making the “Add to Cart” button brighter will lead to an increase in the number of people adding items to their shopping carts.īy having the two websites active at once and randomly directing users to one or the other, the online retail company can monitor the impact of making the “Add to Cart” button brighter and then draw conclusion accordingly. Typically in A/B testing, the variant that gives higher conversions is the winning one, and that variant can help optimize a web site for better results. So to keep it short and simple A/B tests is the application of statistical hypothesis testing which consist of a randomized experiment with two variants, A and B. Even though A/B testing can be used for any experiments it is often used in the digital marketing world (websites, apps, email campaign…)

Bar Chart – Conversion Rate with Upper/Lower limit for the two groups.Table – Conversion Rate with Upper and Lower limit for the two groups.Table – Z-score, Uplift Lower/Upper, P-value and Power.Confidence Interval and Test type Slicers & Uplift and P-value KPIs.Line Chart – The number of orders Control vs Var.Line Chart – The number of visits Control vs Var.Why using Power Bi instead of R/Python?.To find the probability of LARGER z-score, which is the probability of observing a value greater than x (the area under the curve to the RIGHT of x), type: =1 - NORMSDIST (and input the z-score you calculated). Then, to calculate the probability for a SMALLER z-score, which is the probability of observing a value less than x (the area under the curve to the LEFT of x), type the following into a blank cell: = NORMSDIST( and input the z-score you calculated). To make things easier, instead of writing the mean and SD values in the formula you could use the cell values corresponding to these values. Now to calculate the z-score type the following formula in an empty cell: = (x – mean) /. For example, if the range of scores in your sample begin at cell A1 and end at cell A20, the formula = STDEV.S (A1:A20) returns the standard deviation of those numbers. Next, you mush calculate the standard deviation of the sample by using the STDEV.S formula. To calculate the z-score of a specific value, x, first you must calculate the mean of the sample by using the AVERAGE formula.įor example, if the range of scores in your sample begin at cell A1 and end at cell A20, the formula =AVERAGE(A1:A20) returns the average of those numbers.
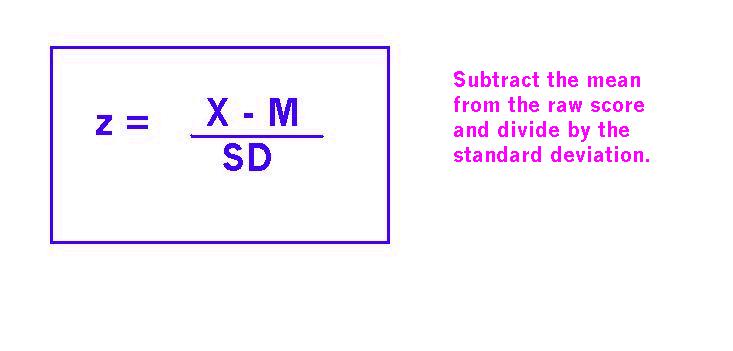
If there is less than a 5% chance of a raw score being selected randomly, then this is a statistically significant result. The probability of randomly selecting a score between -1.96 and +1.96 standard deviations from the mean is 95% (see Fig. Proportion of a standard normal distribution (SND) in percentages. For example, there is a 68% probability of randomly selecting a score between -1 and +1 standard deviations from the mean (see Fig. The SND allows researchers to calculate the probability of randomly obtaining a score from the distribution (i.e. Therefore, one standard deviation of the raw score (whatever raw value this is) converts into 1 z-score unit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
